Land Surveying
Drones in land surveying capture high-resolution aerial imagery, enabling precise mapping, topography analysis, and terrain modeling, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in survey data collection.
Benefits Of Land Surveying
Accuracy and Precision
Drones equipped with advanced sensors and cameras can capture high-resolution images, providing accurate and detailed data for surveying purposes. Integration with GPS technology enhances the accuracy of drone surveying, allowing for precise mapping and measurements.
Safety
Drones eliminate the need for surveyors to physically access difficult or hazardous terrain, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Drones can reach and survey areas that may be challenging for surveyors to access on foot or with traditional methods.
Flexibility
Drones can navigate through diverse landscapes, including rugged or inaccessible terrain, providing flexibility in surveying different types of land. Drones can be used for a wide range of surveying applications, such as topographic mapping, construction site monitoring, agricultural assessments, and environmental monitoring.
Using Drones
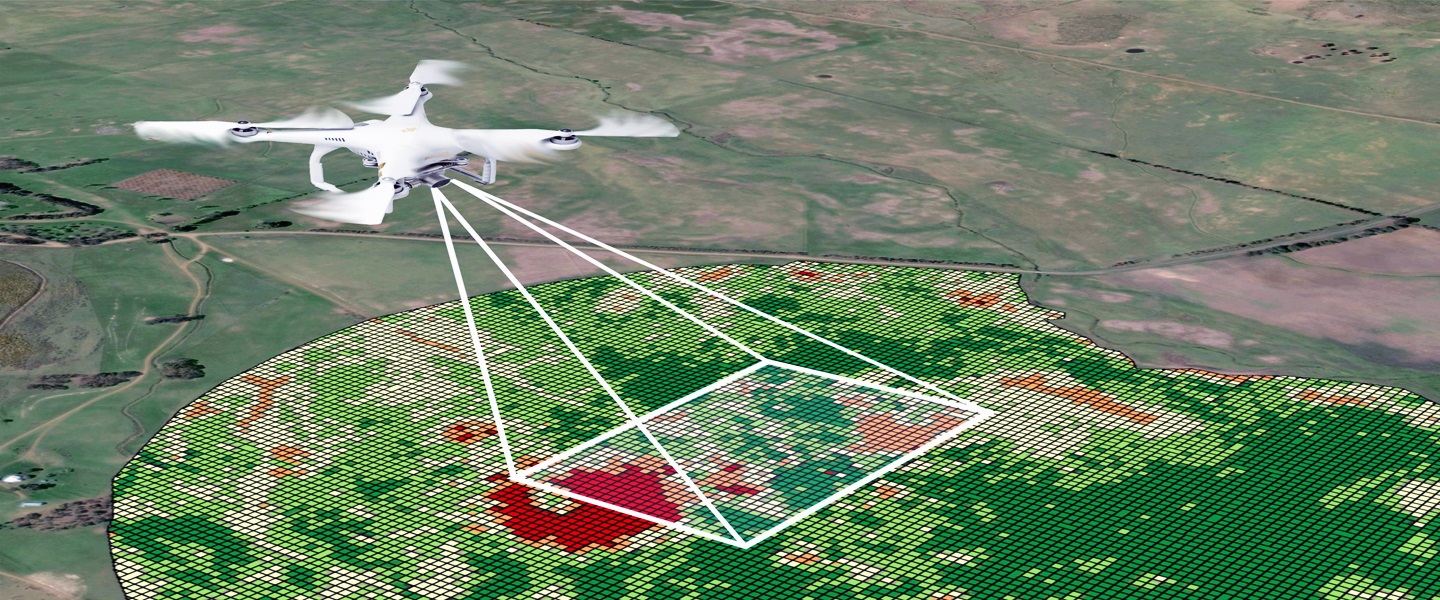
Challenges
- Regulatory Compliance:Adhering to evolving aviation regulations and obtaining necessary permissions for drone flights can be challenging.
- Weather Conditions: Unpredictable weather, such as high winds or rain, can hinder drone operations and affect data quality.
- Limited Payload Capacity: Drones may have restrictions on payload capacity, limiting the types of surveying equipment and sensors that can be carried.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring precise georeferencing and data accuracy can be challenging, particularly in areas with poor GPS signals.
- Battery Life: Limited battery life imposes constraints on flight duration, necessitating careful planning for large survey areas.
- Data Processing Complexity: Handling and processing large datasets generated by drone surveys requires specialized software and expertise.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Drones may encounter obstacles like buildings or trees, requiring advanced obstacle avoidance systems to ensure safe and uninterrupted survey flights.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Drones may encounter obstacles like buildings or trees, requiring advanced obstacle avoidance systems to ensure safe and uninterrupted survey flights.
How Works
- Mission Planning: Define the survey area and objectives. Plan the drone’s flight path using specialized software, considering factors like altitude,overlap, and ground resolution.Consider regulatory requirements and obtain necessary permissions for the flight.
- Takeoff and Data Capture: Launch the drone at the designated starting point. The drone follows the pre-programmed flight path, capturing images or data at regular intervals. Utilize various sensors like RGB cameras, infrared cameras, LiDAR, or multispectral sensors to collect relevant information.Ensure the drone is in proper working condition.Calibrate sensors and instruments for accurate data collection. Verify weather conditions are suitable for flying.
- Real-time Monitoring: Monitor the drone’s flight in real-time to ensure it follows the planned trajectory. Address any issues or adjust the flight path if necessary.
Data Post-Processing:
Transfer captured data to a computer for post-processing. Use specialized software to stitch together images, correct distortions, and create a comprehensive dataset.Georeference the data by integrating GPS information, ensuring accurate spatial positioning.
Explore More Content

Land surveying is a crucial process in understanding and mapping the physical characteristics of a piece of land. With the advent of technology, drones have become valuable tools in modern land surveying, revolutionizing the traditional methods and enhancing efficiency.

Post-flight, the collected data undergoes thorough processing. Specialized software is employed to stitch together images, correct distortions, and georeference the data using GPS information. The result is a comprehensive dataset that can be utilized for various applications, including urban planning, construction projects.
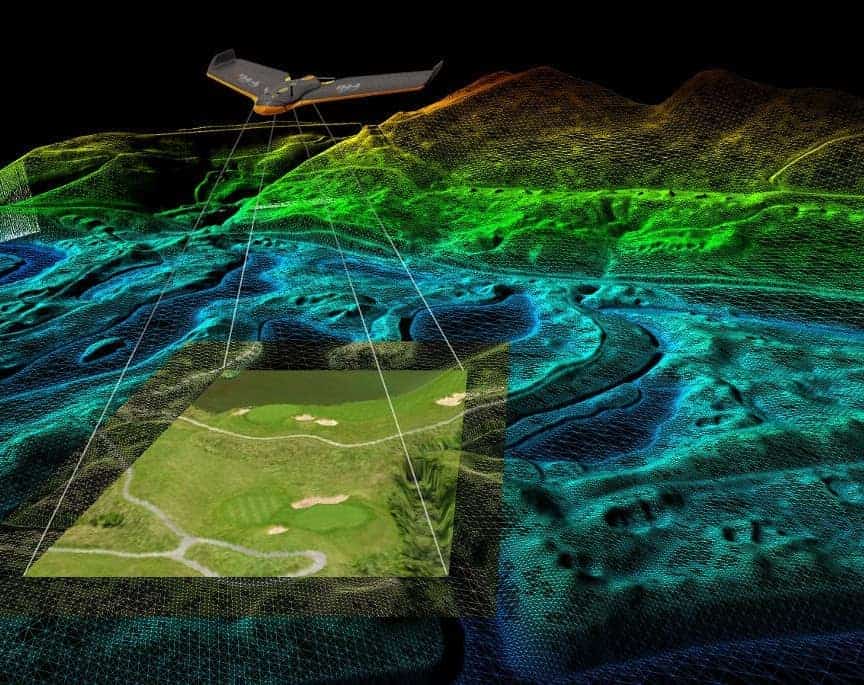
Drones, equipped with advanced sensors such as cameras, LiDAR, and GPS, are deployed to capture high-resolution aerial imagery and collect geospatial data over a specified area. This data includes detailed topographical information, elevation data, and other relevant features of the terrain. The drone’s flight path is meticulously planned using specialized software, considering factors like altitude, overlap, and ground resolution.

The advantages of using drones in land surveying are evident. They provide a cost-effective and time-efficient solution, covering large areas in a fraction of the time compared to traditional surveying methods. The high-resolution data obtained enables detailed analysis and accurate mapping, aiding in decision-making processes for infrastructure development or environmental management.